Archimedes
From the Quicksilver Metaweb.
this is a placeholder for Archimedes
Archimedes
From Wikipedia sources
Archimedes of Syracuse (circa 287 BCE -212 BCE), was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, physicist and engineer.
Discoveries
Archimedes is one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. He became a popular figure as a result of his involvement in the defense of Syracuse against the Roman siege in the First and Second Punic Wars. He is reputed to have held the Romans at bay with war engines of his design ; to have been able to move a full-size ship complete with crew and cargo by pulling a single rope; to have discovered the principles of density and buoyancy while taking a bath (thereupon taking to the streets naked calling "eureka" - "I found it!"); and to have invented the irrigation device known as Archimedes' screw.
In creativity and insight, he exceeds any other mathematician prior to the European renaissance. In a civilization with an awkward number system and a language in which "a myriad" (literally ten thousand) meant "infinity", he invented a positional numeral system and used it to write numbers up to 1064. He devised a heuristic method based on statics to do private calculation that we would classify today as integral calculus, but then presented rigorous geometric proofs for his results. To what extent he actually had a correct version of integral calculus is debatable. He proved that the ratio of a circle 's perimeter to its diameter is the same as the ratio of the circle's area to the square of the radius. He did not call this ratio π but he gave a procedure to approximate it to arbitrary accuracy and gave an approximation of it as between 3 1/7 and 3 10/71. He was the first, and possibly the only, Greek mathematician to introduce mechanical curves (those traced by a moving point) as legitimate objects of study. He proved that the area enclosed by a parabola and a straight line is 4/3 the area of a triangle with equal base and height. (This proposition needs to be understood consistently with the illustration below. The "base" is any secant line, not necessarily orthogonal to the parabola's axis; "the same base" means the same "horizontal" component of the length of the base; "horizontal" means orthogonal to the axis. "Height" means the length of the segment parallel to the axis from the vertex to the base. The vertex must be so placed that the two horizontal distances mentioned in the illustration are equal.)
In the process, he calculated the oldest known example of a geometric series with the ratio 1/4: 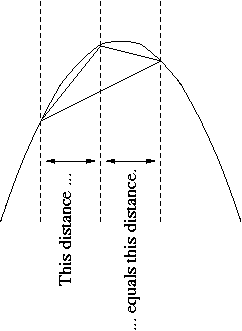
In the process, he calculated the oldest known example of a geometric series with the ratio 1/4:

If the first term in this series is the area of the triangle in the illustration then the second is the sum of the areas of two triangles whose bases are the two smaller secant lines in the illustration. Essentially, this paragraph summarizes the proof. Archimedes also gave a quite different proof of nearly the same proposition by a method using infinitesimals; that different proof is found here.
He proved that the area and volume of the sphere are in the same ratio to the area and volume of a circumscribed straight cylinder, a result he was so proud of that he made it his epitaph.
Archimedes is probably also the first mathematical physicist on record, and the best before Galileo and Newton. He invented the field of statics, enunciated the law of the lever, the law of equilibrium of fluids and the law of buoyancy. (He famously discovered the latter when he was asked to determine whether a crown had been made of pure gold, or gold adulterated with silver ; he realized that the rise in the water level when it was immersed would be equal to the volume of the crown, and the decrease in the weight of the crown would be in proportion; he could then compare those with the values of an equal weight of pure gold.) He was the first to identify the concept of center of gravity, and he found the centers of gravity of various geometric figures, assuming uniform density in their interiors, including triangles, paraboloids, and hemispheres. Using only ancient Greek geometry, he also gave the equilibrium positions of floating sections of paraboloids as a function of their height, a feat that would be taxing to a modern physicist using calculus.
Apart from general physics he was an astronomer, and Cicero writes that in the year 212 BCE when Syracuse was raided by Roman troops, the Roman consul Marcellus brought a device which mapped the sky on a sphere and another device that predicted the motions of the sun and the moon and the planets (i.e. a planetarium) to Rome. He credits Thales and Eudoxus for constructing these devices. For some time this was assumed to be a legend of doubtful nature, but the discovery of the Antikythera mechanism has changed the view of this issue, and it is indeed probable that Archimedes posessed and constructed such devices. Pappus of Alexandria writes that Archimedes had written a practical book on the construction of such spheres entitled On Sphere-Making.
Archimedes' works were not very influential, even in antiquity. He and his contemporaries probably constitute the peak of Greek mathematical rigour. During the Middle Ages the mathematicians who could understand Archimedes' work were few and far between. Many of his works were lost when the library of Alexandria was destroyed and survived only in Latin or Arabic translations. As a result, his mechanical method was lost until around 1900, after the arithmetization of analysis had been carried out successfully. We can only speculate about the effect that the "method" would have had on the development of calculus had it been known in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Writings by Archimedes
- On the Equilibrium of Planes (2 volumes)
This book spells out the law of the lever and uses it to calculate the areas and centers of gravity of various geometric figures. * On Spirals
In this book, Archimedes defines what is now called Archimedes' Spiral. This is the first mechanical curve (i.e., traced by a moving point) ever considered by a Greek mathematician. Using this curve, he was able to square the circle. * On the Sphere and The Cylinder
In this book Archimedes obtains the result he was most proud of: that the area and volume of a sphere are in the same relationship to the area and volume of the circumscribed straight cylinder. * On Conoids and Spheroids
In this book Archimedes calculates the areas and volumes of sectios of cones, spheres and paraboloids. * On Floating Bodies (2 volumes)
In the first part of this book, Archimedes spells out the law of equilibrium of fluids, and proves that water around a center of gravity will adopt a spherical form. This is probably an attempt at explaining the observation made by Greek astronomers that the Earth is round. Note that his fluids are not self-gravitating: he assumes the existence of a point towards all things fall and derives the spherical shape. One is led to wonder what he would have done had he struck upon he idea of universal gravitation. In the second part, a veritable tour-de-force, he calculates the equilibrium positions of sections of paraboloids. This was probably an idealization of the shapes of ships' hulls. Some of his sections float with the base under water and the summit above water, which is reminiscent of the way icebergs float, although Archimedes probably wasn't thinking of this application. * The Quadrature of the Parabola
In this book, Archimedes calculates the area of a segment of a parabola (the figure delimited by a parabola and a secant line not necessarily perpendicular to the axis). The final answer is obtained by triangulating the area and summing the geometric series with ratio 1/4. * Stomachion
This is a Greek puzzle similar to Tangram. In this book, Archimedes calculates the areas of the various pieces. This may be the first reference we have to this game. Recent discoveries indicate that Archimedes was attempting to determine how many ways the strips of paper could be assembled into the shape of a square. This is possibly the first use of combinatorics to solve a problem. * Archimedes' Cattle Problem
Archimedes wrote a letter to the scholars in the Library of Alexandria, who apparently had downplayed the importance of Archimedes' works. In these letters, he dares them to count the numbers cattle in the Herd of the Sun by solving a number of simultaneous diophantine equations, some of them quadratic. This problem is one of the famous problems solved with the aid of a computer. * The Sand Reckoner
In this book, Archimedes counts the number of grains of sand fitting inside the universe. This book mentions Aristarchus' theory of the solar system, contemporary ideas about the size of the Earth and the distance between various celestial bodies. From the inroductory letter we also learn that Archimedes' father was an astronomer. * "The Method"
In this work, which was unknown in the Middle Ages, but the importance of which was realised after its discovery, Archimedes pioneered the use of infinitesimals, showing how breaking up a figure in an infinite number of infinitely small parts could be used to determine its area or volume. Archimedes did probably consider these methods not mathematically precise, and he used these methods to find at least some of the areas or volumes he sought, and then used the more traditional method of exhaustion to prove them. This particular work is found in what is called the Archimedes Palimpsest.
Archimedean spiral
| Archimedian_spiral.png |
An Archimedean spiral is a curve which in polar coordinates r,θ can be described by the equation r = a + bθ with real numbers a and b. Changing the parameter a will turn the spiral, while b controls the distance between the arms.
This Archimedean spiral is distinguished from the logarithmic spiral by the fact that successive arms have a fixed distance (equal to 2π b if θ is measured in radians), while in a logarithmic spiral these distances form a geometric progression.
Note that the Archimedean spiral has two arms, one for θ > 0 and one for θ < 0. The two arms are smoothly connected at the origin. Only one arm is shown on the accompanying graph. Taking the mirror image of this arm at the y axis will yield the other arm.
Sometimes the term Archimedean spiral is used for the more general group of spirals

The normal Archimedean spiral occurs when x = 1. Other spirals falling into this group include the hyperbolic spiral, Fermat's spiral, and the lituus. Virtually all spirals appearing in nature are logarithmic spirals, not Archimedean ones.